A financial statement template is used to capture and present facts about a company’s financial position in an orderly and easy-to-follow manner. This template typically includes critical financial documents: the income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flow. Every part of the template has its purpose and functions to summarize the revenues and expenses of the business, illustrate details of assets and liabilities, and identify the flow of cash in and out of the business.
Using the financial statement also means that reporting is always properly formatted. As a result, it is easier to compare the financial standing of an enterprise at different periods of its existence. Following the standard format is a great advantage because it ensures that the organization clearly passes information on to stakeholders, investors, and even regulatory bodies.
Download Free Simple Financial Statement Templates
What is a financial statement?
A financial statement is a formal record of the financial activities and position of a business, organization, or any person. It provides an overview of financial performance over a specific period, often quarterly or annually, and comprises several key components: the income statement, balance sheet, and the statement of cash flows.
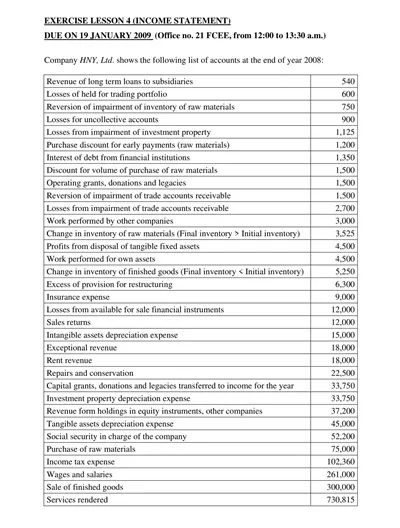
Another document in the financial statements is the income statement, which brings out the company’s competence in revenue and the expense incurred, leading to net income. The very nature of the balance sheet provides a picture of the organization’s assets, liabilities, and equity accounts for a particular period.
Finally, the cash flow statement shows the movement of money in and out of the business, showing a firm’s cash management and working. These documents support all business decision-making processes and help meet legal requirements.
Types of Financial Statements
This paper aims to evaluate the value of financial statements in determining the financial health of an organization. There are four primary types of financial statements that companies typically use:
1. Income Statement
This is also known as the income statement, which outlines the income expenditure and profits in a given duration. With it, the company establishes profitability and efficiency in doing its operations.
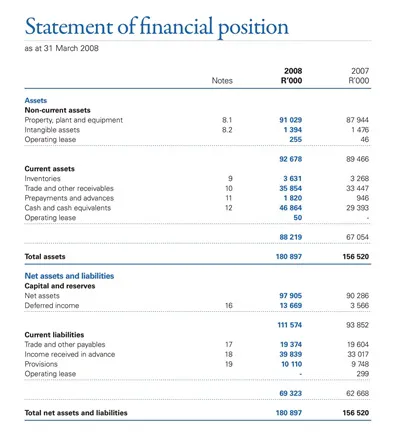
2. Balance Sheet
This statement thus gives a balance sheet view of a company’s financial health at a given period of its operating cycle. It displayed the resources and obligations of that particular company to the shareholders, indicating the amount of resources it possessed and the amount owed to the shareholders.
3. Cash Flow Statement
Flows of money in & out of the business are significant for assessing the company’s liquidity, representing the statement of cash flows. It shows how efficiently an organization makes money to support operating costs and invest in capital projects.
This document shows changes in the equity section of the balance sheet and gives reasons for variations in retained earnings and paid-in capital. It is important to gain an understanding of a company’s equity financing.
All of them are quite helpful to cover the general picture of the financial condition of a given company and to make further strategic improvements if needed.
Components of Financial Statements
Every financial statement includes several parts that provide information about the financial situation of an enterprise. Knowledge of these components facilitates the analysis of an organization’s financial performance and condition.
Income Statement Components
- Revenue: The operating income from the sales of products and services considered normal within an organization.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Out of all cost variables that affect a company, what can be directly associated with manufacturing a company’s products.
- Gross Profit: Computing revenue by COGS shows the level of effectiveness of production and sale of products.
- Operating Expenses: A condition in which certain costs that represent the normal pattern of operations are charged directly to an item or activity.
- Net Income: Net operating income is less fixed costs, taxes, and non-operational income.
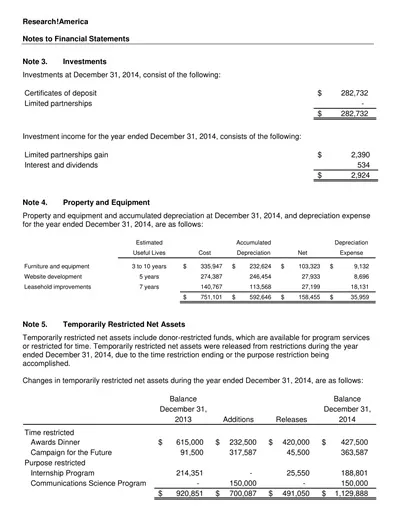
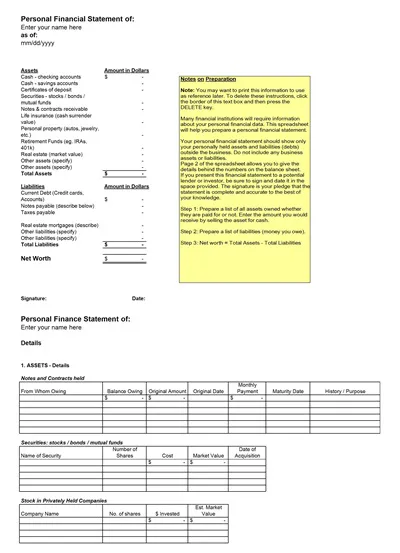
Balance Sheet Components
- Assets: The company’s assets, how it is to value the current assets like cash, inventory, and other assets such as property, plant, and equipment.
- Liabilities: Debt is the amount the company must pay over the short term or within the current financial year and owe over the longer term.
- Shareholder Equity: It is an outstanding interest that an enterprise has in the company’s assets after the elimination of liabilities, regarded by many as the company’s worth.
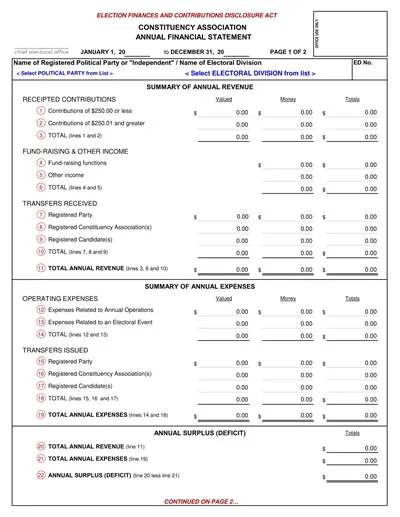
Components of Statement of Cash Flows
- Operating Activities: Cash flows in relation to the activities which are most central to the enterprise or business.
- Investing Activities: This cash flow relates to purchasing and selling long-term investments and property plants and equipment.
- Financing Activities: Cash flows involving the increase and the decrease in size of the entity’s contributed equity capital or borrowings.
- Beginning Equity Balance: The value of the company’s equity at the date of this reporting period.
- Stock Issuance: New equity was mobilized to support the plan during the period.
- Dividends: Dividends are payments made out of profits earned by the company to its shareholders.
- Retained Earnings: Funds that are not paid as dividends and which affect the shareholders’ equity through their reinvestment in the business.
Altogether, these components clearly indicate cash flow within a business establishment, which is important for companies and outside analysts such as investors and government agencies.
Importance of Accurate Financial Reporting
The discipline of properly preparing and presenting financial statements is essential to the lasting relationship that an organization and its investors, creditors, and relevant stakeholders uphold. It provides credibility in financial performance and position, which will help in decision-making.
Analyzable reports assist in evaluating a company’s previous performance, future financial position, and management efficiency. They are important for the company to meet legal and regulatory standards to avoid legal consequences as well as the company’s reputation.
Furthermore, accurate financial statements increase organizational credibility to its key stakeholders and the general public with regard to the organization’s financial position, and hence, it can easily obtain financing to finance its operations. Last, it helps in planning and management to enable organizations achieve their growth and development.
How to Read and Interpret Financial Statements
In other words, it considered all the documents’ parts to derive information on the performance and the financial strength of the companies in question. Here are key steps to guide the process:
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Terms: It helps to know that assets are things you own, liabilities are things you owe, equity is how much of the business you own, revenue or sales is how much money you make, and expenses are how much it costs you.
- Evaluate the Income Statement:
- The revenue figures should be analyzed to determine how the company’s sales have been over some period of time.
- The COGS should be analyzed to measure the efficiency of the production line.
- Examining operating expenses to determine the company’s measures to manage its expenses.
- The evaluation of absolute gross profit and net income for the company should be performed to look for profitability trends and pay attention to the profit margins.
- Examine the Balance Sheet:
- The company’s liquidity should be analyzed by comparing current assets and current liabilities.
- Over time assets and liabilities should be analyzed to see the structure of capital that the company has adopted.
- Review the balance of shareholders’ equity and find out the available amount for shareholders.
- Assess the Cash Flow Statement:
- It emphasizes the operating activities to assess cash flow originating from the company’s main business operations.
- Analyze the investing activities to find out how the company invests in the growth of the company.
- Assess the financing activities to gain insights into the company’s capacity to finance its activities and investments.
- Study the Statement of Shareholder Equity:
- Pay attention to fluctuations of equity that occur as a result of issuing new stocks or repurchasing them.
- Understand how retained earnings might affect future investment or dividend policies or otherwise.
- Look for Trends and Patterns:
- Compare several periods to determine positive or negative patterns, like a steady increase in revenue or, on the contrary, a decrease in margins.
- It is also good to compare certain solace, such as the debt to equity or the return on equity to the industry average.
- Consider External Factors:
- Have knowledge of matters concerning the industry affecting the financial performance of the queue company.
- Thinking of current events or news, how could strategies be effective or ineffective in future outcomes?
The basic steps are fundamental to creating the foundation for further assessments of a company to determine its financial position and possible performance in the future.
How to Create a Financial Statement Template
One of the vital first steps in managing the process of financial reporting involves developing a template for a financial statement. Below are the steps you can follow to develop an effective template:
1. Define the Purpose and Scope
First, decide what financial reports you want to generate: income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement, and when, in terms of periods, they should be produced. Defining the scope will set the premise for the design process and guarantee that the template addresses all necessary reports.
2. Collect the Necessary Data Compositions
Find all the information that should be embodied in each statement. An income statement might encompass revenues, cost of sales, operating expenses, and taxes. The balance sheet presents all assets, liabilities, and equity accounts. Where necessary, support the completeness of data by referring to the code of as regulation or internal reporting system.
3. Select a Proper Software Application
Choose Excel, Google Sheets, or specific accounting software because they should make your template. Inventory accuracy and optimization These tools are flexible, easy to use, and will perform most of the calculations automatically when fed with data, thus eliminating avoidable data entry errors.
4. Design the Template Structure
It is important to arrange the layout of each financial statement in a sequential manner. For instance, in an income statement, the format follows revenue, expenses, and net income. Headings should be clearly visible and labeled to help create a clear navigation system and to follow an acceptable format.
5. Include Formulas for Automated Calculations
Use formulas to develop other important values such as profit margins, total assets, liabilities, and equity. This minimizes human interference, and it is apparent that changes in the input data have been captured to reflect these statements.
6. Add Sections for Comparative Analysis
If necessary, add sections for data from previous periods so that comparisons can be made if necessary. This is especially important when one wants to compare the company’s financial performance at different times.
7. Validate with a Test Run
Testing the template with real numbers is also recommended to ensure that it will precisely record all related data. Organise modifications according to the received feedback with reference to how it can be improved to improve its performance and satisfy user expectations.
By doing all these, you will have a well-designed template for the financial statement that optimizes the positive elements of the consistency of financial reporting.