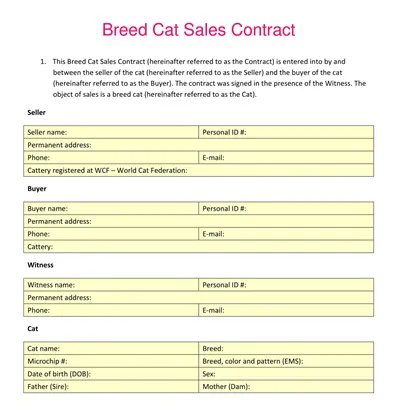
A Sales Contract Template is a pre-made document that outlines the agreed-upon terms and conditions that have been made between a buyer and a seller for the acquisition of any goods or services to be delivered.
It generally contains such details as the description of the goods or services, price, payment terms, delivery schedule, warranties, and the procedures to resolve any disputes. The template operates as a legal agreement meant to safeguard the interests of the parties involved because it sets out their rights and legal duties.
Download Free Sample Sales Contract Templates
What is a Sales Contract?
A sales contract, also called a sale of real property contract, is a legal agreement that is effective between a buyer and a seller that discloses the details of the sale of some rights and/or benefits. It outlines important terms of the deal, such as the goods or services description, the price, payment terms, delivery instructions, the warranty, and the duties and liabilities of both parties.
A sales contract benefits both the buyer and the seller by outlining what each is required to do, thus avoiding arguments and misunderstandings. It is an important document in business transactions, as both parties have a clear, binding understanding of the agreement.
Key Elements of a Sales Contract
A Sales Contract must include various important stipulations so that it is understandable, legally binding, and capable of protecting the purposes and interests, respectively, of the buyer and the seller.
Here are the key elements:
- Details of the Parties: Both parties will have to show their full names, addresses, and contact information.
- Detailed Description of the Goods or Services: A clear description of what the buyer will receive and the entitlement to this description, such as weight, quantity, quality, model numbers, specifications, or the type of services to be provided.
- Purchase Price and Payment Terms: The agreed price needs to be given and along with the payment terms (method of payment, payment schedule, and any applicable taxes or fees).
- Delivery Terms: Details of how, when, and where the goods or services will be handed over to the customer.
- Warranty and Guarantee: Warranties and guarantees of goods or services should be described, including their terms and conditions.
- Inspection and Acceptance Conditions: Terms giving the buyer the right to inspect goods or services before final acceptance and ways for rejecting defective items.
- Transfer of Risk/Title: Clearly states at which point the ownership and the risk of loss or damage are transferred by the seller to the buyer.
- Return, Exchange, and Refund Procedures: Sets out the circumstances in which goods can be returned or exchanged or returned for a refund, deadlines for actions, and procedures.
- Breach of Contract & Remedies: States what kind of actions amount to breach of the contract and gives a mention of the legal remedies to which the non-breaching party is entitled.
- Dispute Resolution/Governing Law Section: States in which disputes shall be arbitrable (negotiation, arbitration, or lawsuit) and what law shall govern the agreement.
- Force Majeure Clause: Looks out for both parties from the blame if unforeseen events (like earthquakes or country instability) stop them from meeting the contract.
- Confidentiality Clause (if): Confirms that any sensitive information encountered by the parties included in the transaction is confidential.
- Amendment and Termination Terms: Specifies the terms according to which the contract can be amended or terminated, stipulating which notice periods apply.
- Signatures of Both: The agreement signed, dated, and must be signed by an authorized representative of the buyer and the seller to be binding legally.
By including all these terms, the sales contract becomes a guardian against disputes and fully safeguards both parties.
Types of Sales Contracts
Sales contracts vary according to the kind of transaction being completed and the type of needs of the parties that are getting into an agreement. Here are the main types:
Bilateral Sales Contract
A bilateral sales agreement is characterised by reciprocal promises made by the Buyer and the Seller. The seller undertakes to hand over the goods or the performance of the services, and the buyer undertakes to accept the same and pay the price so determined. This is the regular sales contract used for most business transactions.
Unilateral Sales Contract
In a unilateral sales contract, only one party makes a promise which, by its very nature, generates a BOOT obligation on and becomes binding to its obligee, but only on the occurrence of a specific cause or act by its obligee. An example is that a seller gives a bounty on a product if purchased under some specific terms and is bound by it once the buyer completes the purchase.
Conditional Sales Contract
A conditional sales contract only comes into existence when particular conditions are complied with. Such examples include a buyer agreeing to buy a piece of property or merchandise pending receiving loan approval, in addition to other necessary approvals.
Installment Sales Contract
An installment sales contract lets the buyer’s obligation for products be spread over time through a series of debit payments. Possession may or may not automatically switch over occasionally, based on the terms of that agreement.
Sales Agreement with Warranty
This kind of contract provides particular guarantees by the seller regarding the level of quality, state, or effectiveness of the products or solutions sold. It safeguards the buyer as it offers protection if the product fails to meet the guaranteed criteria.
When Do I Need a Sales Contract?
A Sales Contract is always required when the transaction involves high value, great complexity, or unique conditions, and they are preferably explicitly outlined. A sales contract is when purchasing and/or selling high-priced or bulky products that both parties are legally protected. It is especially important when payment terms are complex, such as monthly payments or post-delay payments, that the schedule and consequences of non-payment will be specified.
A contract is also important when goods are supplied in parts or when goods are custom-made, as it clarifies delivery, quality, and specifications. In addition, if neither the transaction occurs inside the home country nor, for instance, the sale into the United States, you can nonetheless hire the precise lawyer for global transactional work in a globally famous and reputable large law firm with details upon request.
It is also called for when warranties or guarantees are involved in the buy to ensure the buyer is guarded, and also if there are any flaws. If a third party is to be involved, the contract will cover their position and commissions. Through-venture deals contracts are basic all the time, there are accessible claims, or when you have to safeguard both financial and legal interests for a working circumstance.
Advantages of Using a Sales Contract
Drawing up a Sales Contract is helpful for each of the parties in any transaction, as it has some benefits for both parties. These benefits include:
- Clarity and Certainty: A sales contract fully outlines the details of the agreement, including the price, delivery terms, payment profiles, etc. This eliminates any chance of miscommunication or misunderstanding & roles and expectations will be identical for both.
- Legal Protection: A sales contract is just a legally binding document that safeguards both parties. In case either of the parties breaches the contract, it can be presented in Court to compel them to fulfill their set of duties according to the Contract.
- Risk Management: A sales contract defines significant terms like delivery dates, warranties, and payment schedules by stating them clearly; this contract can avoid the variety of risks present in both parties. It can deal with matters such as delayed delivery, faulty products, or late payment and provide a smooth process for the resolution of those issues.
- Payment Assurance: A sales contract specifies how payments are to be made and the timing of such, including the total amount owed and what the installment plan should be. This also ensures that both parties are on the same page regarding credit terms, and an advance payment will be much less likely to be late or missed.
- Delivery and Performance Assurance: Delivery terms outlined by the contract include timelines. This gives both sides assurance that the agreed-upon items or services will materialize as agreed upon.
- Dispute Resolution: Sales contracts usually contain clauses to resolve disputes, whether through mediation the arbitration. If a problem sits in the mix, on the off chance that there is a contract set up, it will help settle the distinction quicker and less expensively, with the goal that legal action is not required.
- Clear Recourse in Case of Breach: The contract spells out what enforcement process occurs if one is not held accountable on the obligations required in the contract. It then furnishes fair recourse, i.e., through, way of, or under compensation, contract deadlock or other assurances; and hence bolevs both of parties clear in regard to consequences.
- Establishes a Professional Relationship: A sales agreement records the sale, doing which fosters professionalism as well as trust between the buyer and the seller. It indicates that ‘we are both keen to comply with the original arrangements and manage this arrangement in a fair and amicable way.
- Protection for Custom or Specialized Goods: If the deal involves sales of custom or specialty products, a sales contract will ensure that every party concerned to be of the particular specifications, degree expectations as well and delivery schedules. This offers security for both parties, should any disputes arise about the product.
- Legal Compliance: A properly prepared sales agreement ensures that you are fulfilling the terms of the agreement with applicable laws and laws, decreasing the possibility of violating them. This is very important in light of international trading or when you are handling firms that are controlled by the regulatory bodies.
Dos and Don’ts of Sales Contracts
In creating or entering into a sales contract, some fundamental circumstances should be adequately followed to make the understanding legally significant and defend both parties. Things to do and not to do are as follows:
Dos of Sales Contracts
Here are some Dos of Sales Contracts:
Do Be Clear and Specific
Clarify the specifics of the deal – the products/services being sold, the price tag, delivery conditions, as well as payment plans. The more precise, the harder for misunderstandings.
Do Include All Relevant Details
See that the contract contains all the necessary details, those being the names and addresses of the parties, descriptions of the goods or services, delivery times, warranties, and any additional terms applicable to the transaction.
Do Use Plain Language
Avoid overly complex legal jargon. The contract should be drafted such that even parties understand the language of the contract easily to execute the terms and conditions easily.
Do Define Payment Terms Clearly
Detail the amount to be paid, the date, and. Method of payment shall be paid (e.g., wire transfer, credit, or check). This also prevents confusion and will prevent late payments.
Do Make a Contingency for Dispute Resolution
Make sure to have a provision in case of disputes, whether from negotiation, mediation, or arbitration. This creates a platform for settling disputes without the use of legal dispute settlements.
Do Address Breach of Contract
Specifically outline the penalties for a breach, including legal action, termination rights, penalty, and like. This way, both parties can be certain as to what takes place if either of them does not live up to their obligations.
Do Hold Copies of the Signed Agreement
Both the buyer and seller should keep signed copies of the sales contract on file. This way also ensures that both parties have the terms agreed to, which were agreed to if a dispute occurs.
Don’ts of Sales Contracts
And here are some Don’ts of Sales Contracts:
Don’t Leave Ambiguities
Steer clear of vagueness as well as unclear terms inside the contract. Since ambiguous terms of language might result in misunderstandings, unenforceable in court.
Don’t Skip the Fine Print
Overlook essential details such as delivery deadlines, artifacts of late payments, and squeezes. These terms are seemingly trivial, but can be highly important in averting disputes.
Don’t Include Unfair Terms
Prevent biased or unfair phrases from one party. A fair contract ensures the interests of both parties, it promotes trust and compliance.
Don’t Miss a Termination Clause
Omitting clauses that outline how the contract can be cancelled or revised will cause future complications if one side wishes to void the contract.
Don’t Ignore Local or Yes Global Laws
Guarantee the contract adheres to proper applicable federal, state, or international laws. Not adhering to legal musts can make the contract invalid or problematic under the law.
Do Not Utilize a Template Without Altering It
While templates can be useful, however, ensure to personalize the contract for the particular transaction. Generic templates may not include the particular details or have provisions that are not relevant to your case.
Don’t Rush the Signing Process
Do not rush. Re-read and understand each segment of the contract before you sign it. Hurry-ing in can cause the omission of important details and the acceptance of poor terms.
By doing so, both the buyer and seller can ensure that their sales contracts are valid, fair, and legally binding. A good contract reduces risks and builds successful business partnerships.
Tips for negotiating terms in a Sales Contract
Negotiating the sales contract is essential to have both parties satisfied and protected. Good negotiation can stop miscommunication and conflicts from arising later. Take note of the following suggestions during the negotiations:
- Understand Your Priorities: Before starting to negotiate, precisely determine your priorities and non-negotiables. This will enable you to stay on track as to what matters, it is price, delivery lead time, payment terms, or warranty.
- Do Your Research: Also, ensure that you know your way around the industry standards, the whole pricing protocol, and commonly used backpacker words for the products and services being offered. This will give you a strong base for negotiation and prevent overclaims.
- Be Ready to Compromise: Negotiation is a give-and-take, and being reasonable can advance your possibilities for working a successful arrangement involving both Social Club Bands and those contacting them. Find out where you can be flexible and be ready to give up on a few things without giving up your main requirements.
- Focus on Win-Win Solutions: Treat the negotiation with a mindset to achieve a win-win result. Strive for terms in your favor, yet useful to the other; indeed payment scheduling arrangement that favors both parties; even a fixed delivery time frame.
- Be Clear About Payment Terms: Make sure to enumerate in payment terms like amount due, when it’s due, and possible method of payment. Talk about here are the payment plan, deposits, or financing offered. Settle on repercussions for tardiness or non-payment.
- Negotiate Delivery Terms and Deadlines: Delivery is very often the key portion of a sales agreement. Denote delivery dates, modes of transportation, and the account charged with shipping costs. Make sure that timetables are overly ambitious and allow for possible delays.
- Include Clauses for Flexibility: If you foresee that the situation might change, then think about whatever contractual adjustment clauses might be agreed upon. For instance, you may wish to include a term that gives the facility to prolong supply times or modify volumes wherever there are unintended setbacks.
- Address Risk and Liability: Deal with and harmonize who will have responsibility for risks connected with the service or product, this includes of issues like damage during distribution, flaws, and product recalls. Be sure that whilst these terms are set out, this is to avoid any arguments more for the future.
- Beware of Penalties and Charges: Do not impose too severe punishments for the breach of contract since it may give the feeling feeling of unease and distrust. Agree to reasonable and proportional penalties in case of breach, and then make sure they are balanced for both parties.
- Consult with Legal Advisors: If the contract is complicated or of a substantial amount, it is wise to solicit the advice of a legal representative. A lawyer can look for potential legal hazards and verify that the contract respects legal needs; they can assist you in modifying phrases that are obscure or very negative.
- Ensure Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure: If confidential info is concerned, consider having confidentiality provisions that shield proprietary information. In electrical, technology, or manufacturing industries, determining which intellectual property is valuable is highly important.
- Be Patient and Take Your Time: Don’t rush the negotiation process. Spending time to fully read and negotiate the terms can help you avoid missing any storyline information. A contract that is well negotiated will ultimately save time and resources in the long run.
By performing this, you can assure the Sales Contract is reasonable, comprehensive, and honest in good faith of both sides, all things considered, a profitable help relationship.
How to Create a Sales Contract Template
Making a Sales Contract Template necessitates constructing a document that specifies the conditions under which a sale or purchase of material or services will be conducted. This template can be applied to numerous transactions so that there is consistency and legal protection for both parties.
Here is a step-by-step guide to assist you in developing a complete as well as effective sales contract template:
1. Know the Purpose of the Sales Contract
First, start by determining the object of the contract, to detail the terms and conditions of a sale between a buyer and a seller.
2. Gather Key Information
Get all required information such as the names and contact details of the parties involved, a description of the goods or services, the price, delivery terms, and payment terms.
3. Draft the Opening Section
Begin the contract with an introductory paragraph that indicates the date, parties to the contract, and nature of the agreement.
4. Define the Goods or Services
Be brief and to the point to explain what is being sold- quantities, models, specifications, or characteristics relevant to the items.
5. Specify Payment Terms
Define how much, when payments are due, what methods of payment are acceptable, and, if applicable, what fines will be charged for late payments.
6. Detail Delivery Terms
List shipping mode, shipping time, shipping charges responsibility, and what to do if shipping is delayed.
7. Include Warranties and Disclaimers
List any warranties of the product or service, or indicate that the sale is “as-is” and no warranties are applied.
8. Address Risk of Loss
Identify when the risk gets passed from the seller to the buyer, typically the day delivery is made or some other agreed point.