An Art Lesson Plan Template is a framework that helps instructors create appealing, orderly, and efficient art lessons. It lists the lesson goals, the resources you will require, the activities you plan to use, the ABCDE chart, and the questions you plan to assess students and yourself.
This template guarantees that lessons are adequately prepared, differentiated, and correspond to the learning curriculum. It also offers an avenue for assessing students’ learning progress and comprehending the subject area, art in this case.
Download Free Art Lesson Plan Templates
What is an Art Lesson Plan?
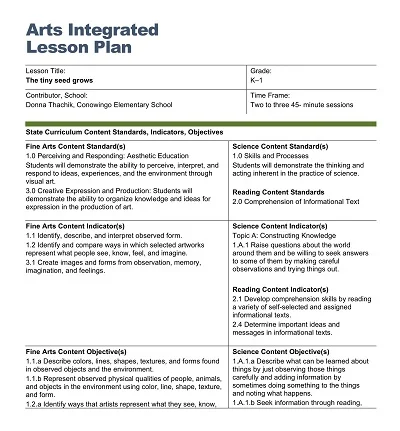
An Art Lesson Plan is a comprehensive document developed by teachers to organize the class. Its components include the lesson’s aims and objectives, the learning resources needed, the lesson’s process, and the expected result.
This mapping chart is instructional in that it lays down the strategic plan to facilitate the lesson. Thus, it guarantees that the educational objectives are met and that students’ learning outcomes are reflected in education by using their creativity, critical thinking, and art appreciation.
Purpose of Art Lesson Plans
Developing art lesson plans is critical in various ways that positively impact students’ learning process. They act as a theoretical map by which the subject is navigated, making education and learning fun while simultaneously being structured.
Below are the essential purposes of integrating art lesson plans into the curriculum:
Educational Structure and Objectives
Educational targets are apparent, and each lesson plan defines specific tasks corresponding to general curriculum targets. The structure should also explain how students acquire skills and knowledge and how they connect.
Encouragement of Creativity
Thus, lesson plans in art education define a set of skills and techniques that can facilitate the students’ creativity while preserving its essence as part of the learning process. The level of freedom and a certain amount of direction instigates creativity and each student’s personality.
Cultural and Historical Context
Including discussions on the sociocultural aspect of artworks assists learners in looking at art from a broader perspective apart from being a beauty. In this regard, the given context enhances the appreciation of art through extended information on how art affects or is affected by society.
Skill Development
Teaching plans in art can aim at creating specific types of artwork, artists’ abilities, and skills associated with straightforward picture drawing and painting and enhanced and sophisticated forms. Skill development is purposely organized to match the student’s growth and competency levels.
Assessment and Feedback
Many lesson plans for structured lessons specify how to assess and give feedback, which is essential for learning. These components enable the teachers to track the child’s progress, evaluate areas of difficulty, and plan an appropriate approach to teaching for each child.
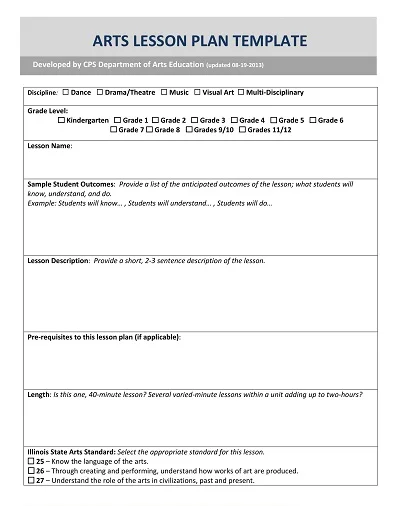
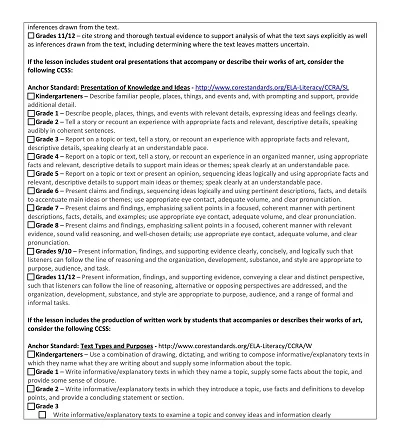
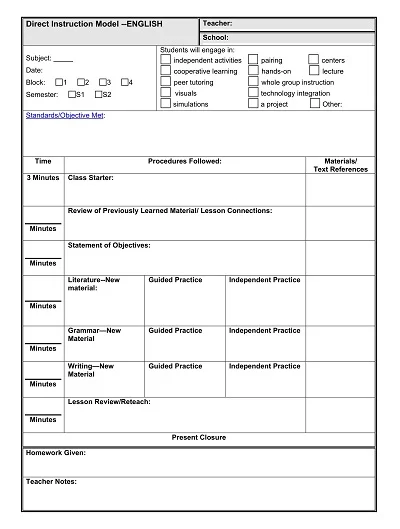
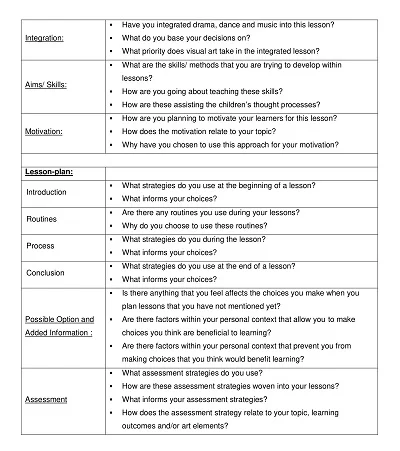
Key Components of an Art Lesson Plan
However, as an art teacher, one has to ensure that the lesson plan is succulent and organized to create a lasting experience for the students. The desired outcomes of a lesson plan should be clear, how to teach the lesson should be determined, the activities to be used in the lesson should be determined, and the checking methods should be chosen. Below, we will focus on the detailed description of significant parts of realizing the art lesson plan.
- Objective: The first recommended step is always to clarify what you want your students to gain from the lesson regarding knowledge. Your goals should document specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound (SMART) features.
- Materials Needed: Enumerate the materials/tools needed in the lesson, such as paints, brushes, canvas, and anything needed to create the artwork, as well as the computer and applications for digital artwork.
- Introduction: In this lesson, the topic has to be briefly explained, or the art concept in focus needs to be defined. This can involve adding historical information about the specific technique, identifying artists famous for using the method or the style the technique is preventing the students from mastering, or adding examples of the style or medium being taught and adaptable to the mentioned technique.
- Instruction: Explain what directions you will give students and provide detailed instructions for every step. This should comprise modeling techniques, lecturing to explain theories, and conducting students through creating artwork.
- Activity: Explain the primary interaction type in which the students use the lesson’s content. Detail what you anticipate the students will produce as the lesson’s conclusion (i.e., a painting or sculpture) and what particular technique or procedure should be included.
- Discussion Questions: Consider questions promoting whole-class discussion and peer negotiation on the art production and the lesson concept. This would assist students in their interaction and comprehension of artwork, allowing them to explain their ideas and emotions regarding their creation and those of others.
- Assessment: Explain the assessment techniques you shall use to assess the student’s work and comprehension of the concepts taught in the lesson. This could be in grades, the pass/fail system, class participation, peer assessment, and self-assessment.
- Closure: It is helpful to have a short wrap-up at the end of the lesson, in which some material involving what was taught could be planned for the next lesson, or some minor activity worked on during the particular lesson.
Benefits of Using Art Lesson Plans
Art lesson plans are essential to ensure education because they provide order to creation and have the following advantages.
1. Enhances Creativity and Expression
Art lesson plans always help the students discover their creativity and uniqueness. This enhances creativity and fosters the students’ freedom in expressing themselves, thus implanting personality.
2. Develops Fine Motor Skills
In the art process, students could use pencils, paints, and clay, among others, in drawing, painting, and modeling, respectively; this assists in developing fine motor activities. This is very helpful in the initial years of learning, helping in the coordination and control that forms part of writing, typing, or any intricate movements.
3. Encourages critical thinking, problem-solving
The use of art results in student’s challenge of reason and increased problem-solving skills. They develop indispensable life skills while articulating or even interpreting art pieces and choosing how to show their ideas.
4. Cultural Awareness and Appreciation
Art education also teaches students about the different art forms that exist worldwide, encouraging the appreciation of culture and history. Thus, this broader view fosters compassion and an understanding of others and the world.
5. Enhances Academic Performance
Evidence shows that when students receive art education, their academic achievement will likely improve. Skills like creativity, concentration, and the ability to follow instructions when doing artwork enhance students’ learning in other areas.
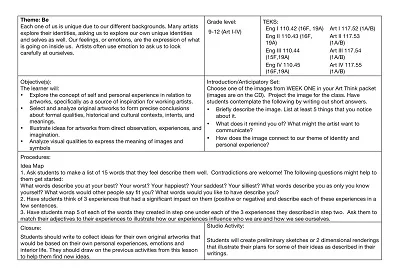
How to Create an Art Lesson Plan Template
Developing an art lesson plan template as described in the lesson plan implies that the lesson plan format is arranged effectively to achieve learning outcomes and, at the same time, use creativity to capture student attention.
Here are the key details to include:
- Objective: The lesson should be anchored with a learning object that defines at the outset what the students must comprehend or be able to carry out by the lesson’s completion.
- Materials Needed: Enumerate all the materials necessary for the lesson, including papers, paints, brushes, and digital tools and software.
- Introduction: Explain how you will ensure you grab the students’ interest and pay attention to whatever is taught in the lesson. This could be a brief discussion / ‘food for thought’ prompt or an art project example.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Describe in detail how the art activity will be done. Ensure they are concise but comprehensive and easy to follow from start to end.
- Demonstration: Explain some necessary procedures or ideas to students before they start their projects. This is especially true with ‘show and tell’ techniques such as diagrams, models, props, or demonstrations.
- Activity Time: Determine the time that students will spend on the art project that you have in mind. Remember to allow adequate time for the students to explore and finish.
- Discussion Questions: Use questions to encourage students to discuss or reflect during an activity or after completing that activity. These questions should make the students ponder more about the work and issues being covered in the lesson.
- Assessment: Explain to the students how their work will be evaluated. Some assessment methods may be formal, while others may be informal.
- Extensions: Suggest ways for students to follow up on the lesson or elaborate on what has been taught in class, probably through other related projects or research areas.
- Reflection: Add a section for the teacher to discuss the lesson and provide instructions on what to do if the lesson is poorly performed.