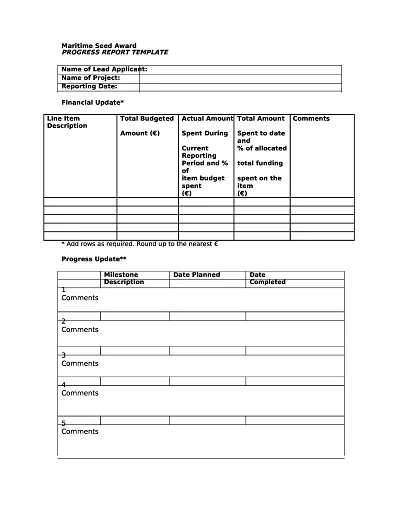
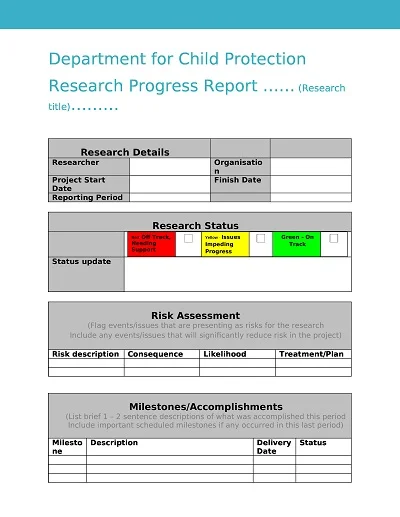
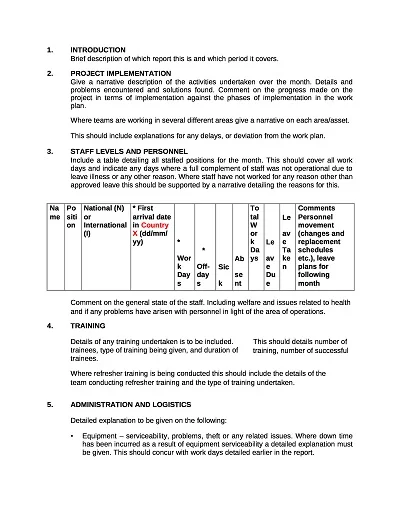
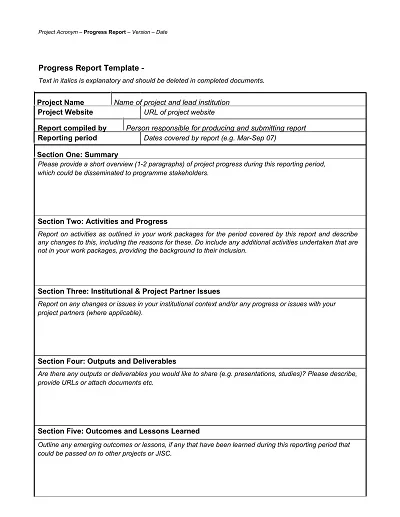
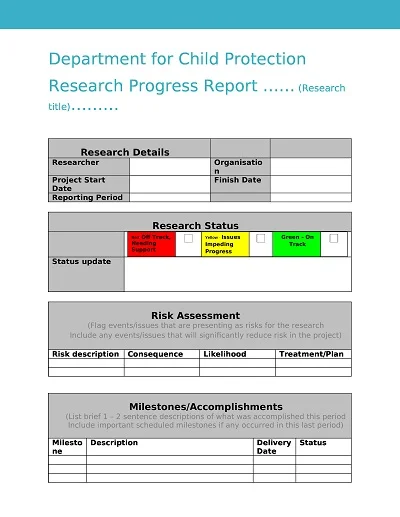
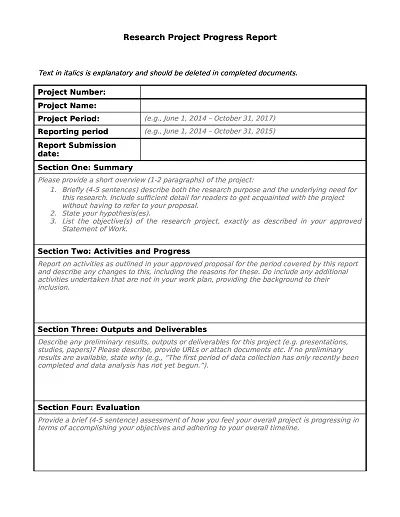
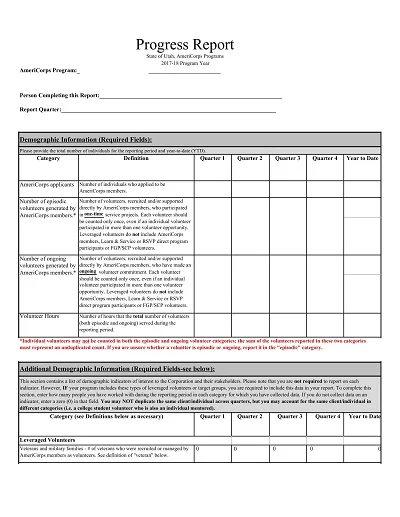
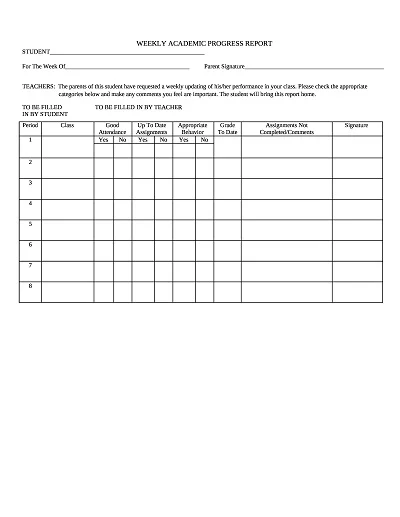
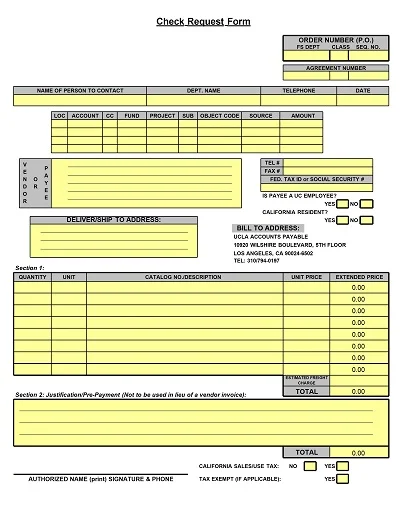
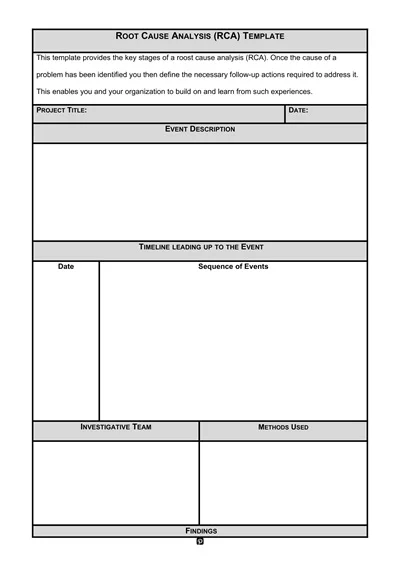
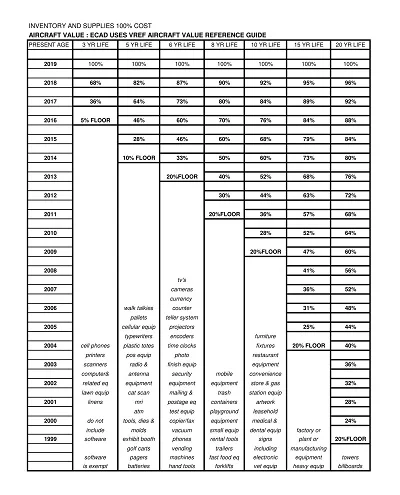
A Progress Report Template is a management tool for tracking and recording the movement of work processes, activities, projects, or tasks over a set timeframe. It normally has sections for objectives achieved, progress made, difficulties encountered, and future outlook.
This template is a documentation tool of the task’s progress between the different members or within other stakeholders and the management team.
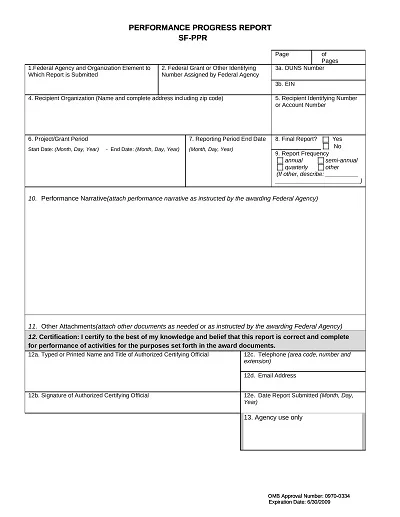
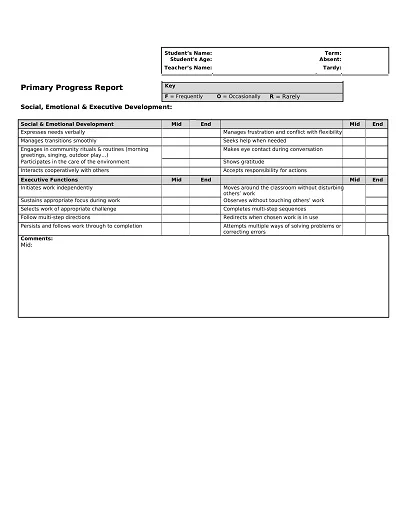
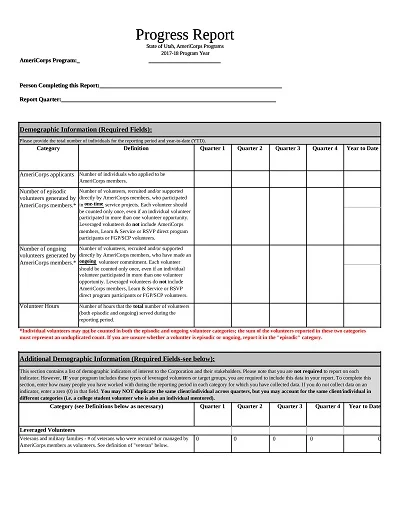
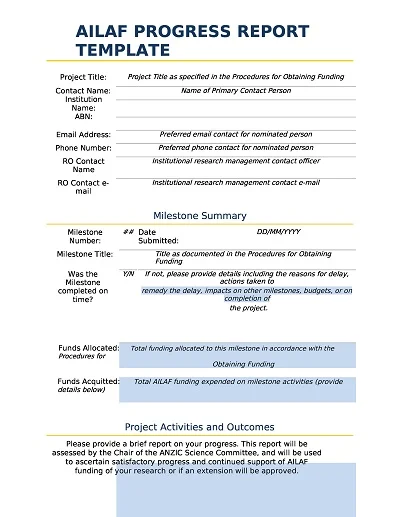
Download Free Example Progress Report Templates
What is a Progress Report?
A Progress Report is a document that demonstrates the state of any project, what has been covered, what is in the pipeline, and what is left.
It is a means of reporting the project status and involving all the stakeholders in reporting every step of the project, including the challenges and any changes that need to be made concerning the project schedule. This report enables an organization to monitor project progress in achieving milestones and delivery within the set time frame.
Purpose and Importance of Progress Report
While operating as the academic coordinator, the author discusses the importance of progress reports for the academic process and points out that they serve several purposes in various areas of professional and academic activity.
Knowledge of what fundamental goals and potential benefits the users of progress reports may work to make the reports relevant and helpful could go a long way toward improving the situation.
Objective Tracking
One of the main uses of progress reports, therefore, is to contain specifics on a project’s objectives and goals. This is especially important for the project management and participants since it allows them to stick to the work schedule and notice certain slowness or shifts that may occur.
Communication Tool
Implementation reports are useful for all project members as they allow for reviewing the project’s status. They help deliver organized information dissemination, communication of concerns, and sharing of accomplishments to ensure effective and productive communication between colleagues, supervisors, and customers.
Performance Evaluation
These reports are crucial in measuring the performance of a single entity and a group. Because the goals set are clear and specific, the amount of progress towards them measured is also measurable and clear; in this way, it is easier for managers to pin down the positives and negatives that they want to discuss with the assessees/subordinates.
Decision-making Aid
This is because detailed progress details provide decision-makers with more adequate guidance on the project’s course. Progress reports are important in that they provide information to interpret performance and improve strategy, resource allocation, and priorities.
Record Keeping
Third, progress reports are the official documentation of the project’s progress and history at a particular time. It is always useful to have documenting resources readily available; this documentation is perfect for reference at any future date and for planning purposes, such as logistics for another project, an audit, or when there are legal conflicts.
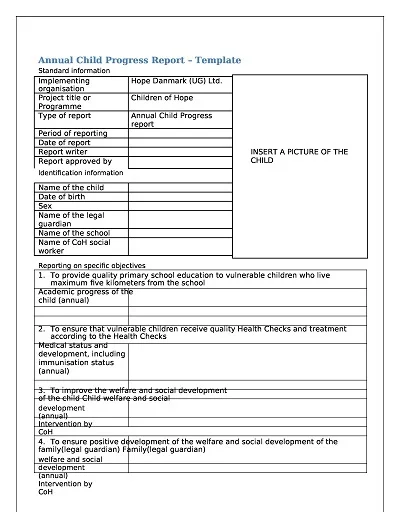
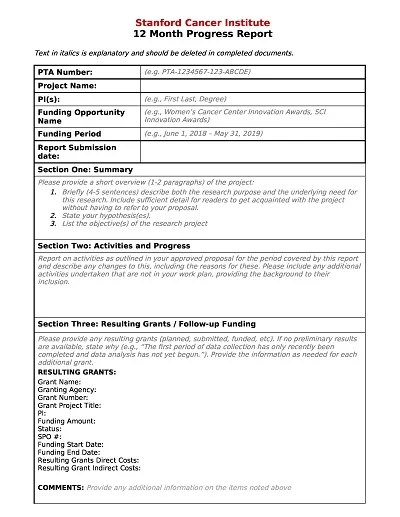
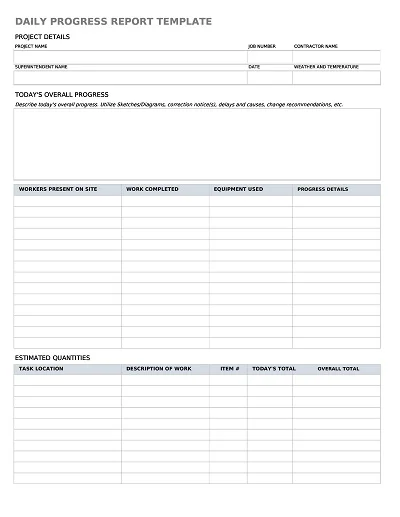
Critical Elements of a Progress Report
Here are the key elements of a progress report:
- Introduction: The progress report includes an outline of the general description of the project, goals, and the importance of this particular period.
- Project Status Summary: A brief and general view of today’s project, including the output and accomplishments made so far or the days/weeks/months behind the schedule.
- Detailed Work Completed: Claims of various caregiving activities rendered specifically in relation to the reporting period through identification of the tasks performed and the outcomes of the tasks performed.
- Challenges and Solutions: Describe a few of the obstacles met along the way and how they were dealt with.
- Next Steps: Discussion of the actions expected of the project over the next time horizon, changes in the work schedule, and developments expected to take place on the project soon.
- Additional Needs: Assessment of any other additional resource needed to accomplish sub-targets or to cope with emergent difficulties in the perspective progression of the vision.
- Appendices (Optional): Additional documents that offer additional evidence of the progress or illustrate the narrative in other ways, such as graphs/charts or maps/photographs.
How to Provide Feedback on Progress Reports
It is also important to express constructive criticisms on the progress reports, for example, in areas of development. Constructive feedback, in particular, can help facilitate desirable outcomes, recognize good performance, promote positive behaviors, and address areas requiring change. This is how I can conduct this task while meeting the set standards of productivity and supportiveness.
Identify Strengths First
- Be Specific: Include the previous assessment report or brief before the current report to show improvement or new accomplishments. It also indicates that you have set time apart to go through their work and make sure that you follow it very well.
- Encourage Continuation: Emphasizing the positive skill domains fosters self-esteem of the ability, and the endeavor towards sustainability is further promoted.
Address Areas for Improvement
- Focus on the Issue, Not the Person: When letting people know that they have made miscalculations in some areas, it is advisable to concentrate on what needs to be altered rather than indulging in a direct critique of the person. This also helps to remove any bias and deal more with facts, making it easier to handle the feedback as it is not personal.
- Provide Constructive Suggestions: What could be done to better the situation rather than focusing on what was wrong and what was done wrong? The positive frame of this approach transforms feedback into the use of constructive criticism.
Set Specific Goals
- Collaborate on Goal Setting: Sit with the person and help him/her establish realistic behavioral goals and targets for change. This also means that both travelers and hosts concur and perceive the objectives as realistic.
- Use SMART Goals: The goals must be clear, well-defined, and quantifiable if achieved within a certain time frame. The lack of clear and measurable targets is another benefit because this framework is useful in developing clear and tangible objectives.
Follow Up
- Schedule Check-Ins: Agree on dates for follow-up appointments to discuss progress in realizing the goals. Sustaining them is beneficial because it gives them energy and ensures they are not disregarded because their value is still recognized as important.
- Encourage Open Communication: Ensure the audience knows they can ask questions, clarify issues, or raise concerns regarding the feedback provided or the general progress report. This, in turn, will foster a favorable environment for growth and development.
By following these guidelines, the things stated in the progress reports become constructive criticism, which can motivate change rather than discouragement.
How to Create a Progress Report Template
Several stages must be taken to design a progress report template. The goal is to formulate a progress report that conveys the project’s overall picture, the problems’ prognosis, and measures for their solution.
Here are the detailed steps to create a comprehensive progress report template:
- Title Page: This section should include the project name, date of the report, name of the report’s preparer, and the project manager’s name.
- Table of Contents: Extended reports usually contain a table of contents to assist the readers with locating particular items in the text.
- Executive Summary: To do this, review the project’s activities, milestones completed and/or yet to be achieved, and issues encountered.
- Project Overview: Step one involves giving project details, such as goals and projected results, before starting the process.
- Achievements: Enumerate the achievements and work done to complete a specific report period.
- Challenges and Issues: Describe any issues faced or barriers met, their action plan, and how they were dealt with or needed to be handled.
- Next Steps: Describe the activities foreseen for the subsequent period, the timeline for their implementation, and the identification of performers.
- Appendices: This is where you add any extra facts, figures, graphs, or information that might go into the report but may be considered too much for the main sections.