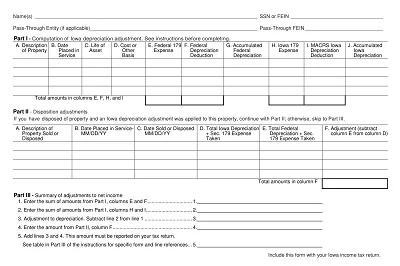
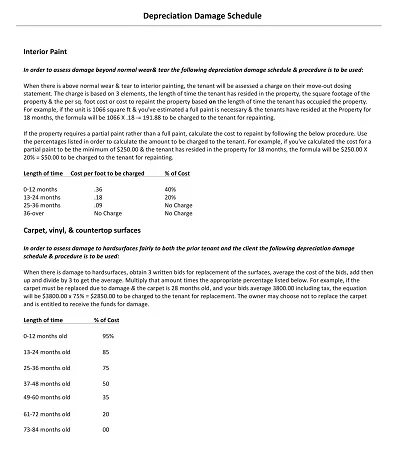
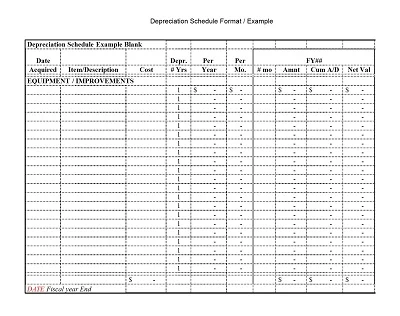
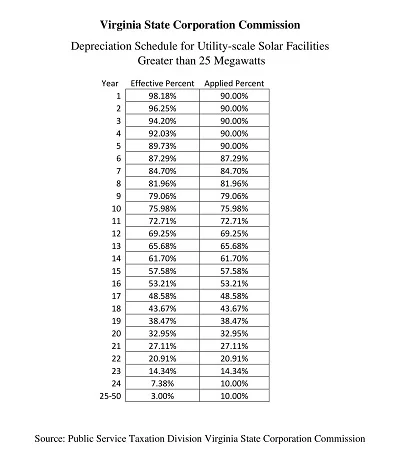
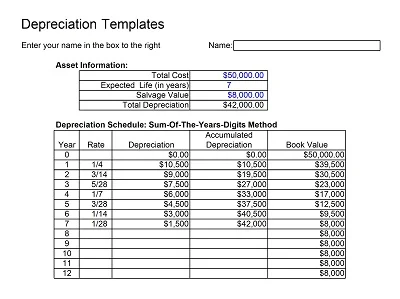
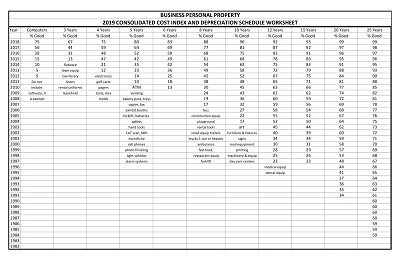
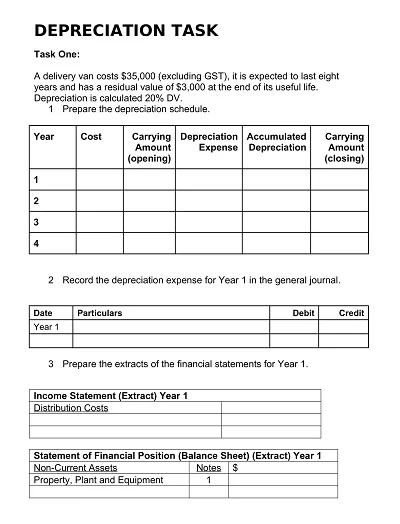
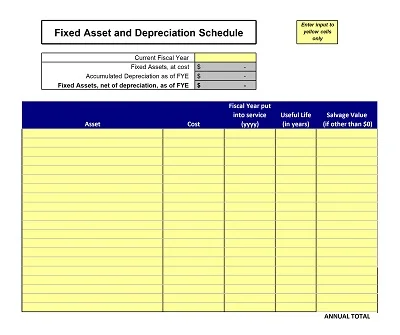
Depreciation is an asset’s monetary value reduction when it is used. Hence, a Depreciation Schedule Template is a tool designed to help track depreciation and predict it in the future.
It ensures that only accurate and structured data regarding the asset’s cost, estimated salvage value, useful life, and the most appropriate depreciation method is captured. Hence this template comes in handy to reduce the computational computations when it comes to depreciation and also present a graphical presentation of the difference in asset depreciation.
The template is helpful in the preparation of accounting records and safeguards compliance with accounting principles; when used, it eases the development of overall financial and tax strategies.
This is a historical record of the value of the assets, providing a way to make better decisions on asset management and investments. For its preparation, a company often uses it to manage its finances through budgeting, filing tax returns, and auditing.
Download Free Simple Depreciation Schedule Templates
Benefits of Using a Depreciation Schedule
Utilizing a depreciation schedule in your business has a lot of advantages, which play a very important role in its health. Let us discuss these benefits and how they can be a plus to your business concerns operationally and financially.
Financial Planning
It is always important to ensure that estimates for using fixed assets are consistent and accurate, as this gives a better appreciation of the actual cost within a given period.
This information allows you to track your financial position and plan for necessary expenses well in advance to ensure that the required cash is available when needed; It also enables you to determine the most appropriate time to replace or renovate any asset.
Tax Implications
A proper depreciation schedule is an essential feature to any business that is in a bid to schedule tax deductions and reports properly.
They ensure that they are pulling out the full tax benefits and that depreciation expenses calculated and reflected in the financial statements align with the agreed tax standards.
Asset Management
By taking depreciation frequency and always keeping a record of the depreciation, you are, in fact, controlling the life cycle of each asset and the overall business capital in return.
This places you in a privileged position to effectively manage the problem resources, make sound sale or replacement decisions, and even coordinate the investment portfolio with the corporate path.
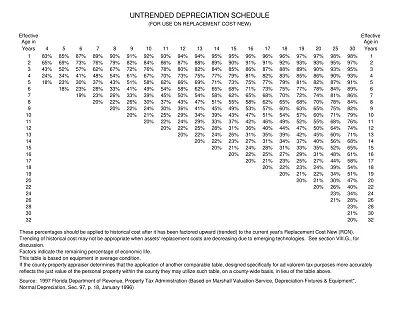
Types of Depreciation Schedule
These depreciation schedules may differ depending on the company’s industry, the specifics of the assets, and internal management approaches. However, below are the widely recognized types of depreciation schedules:
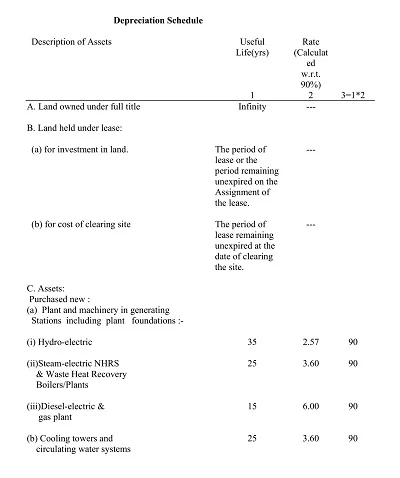
1. Full Depreciation Schedule
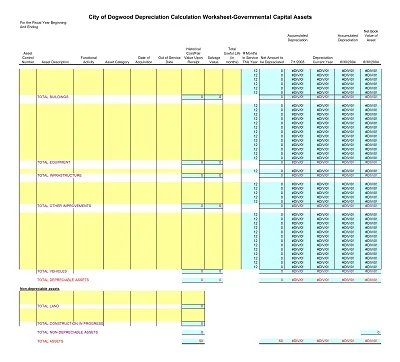
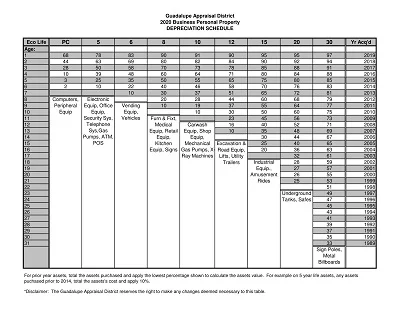
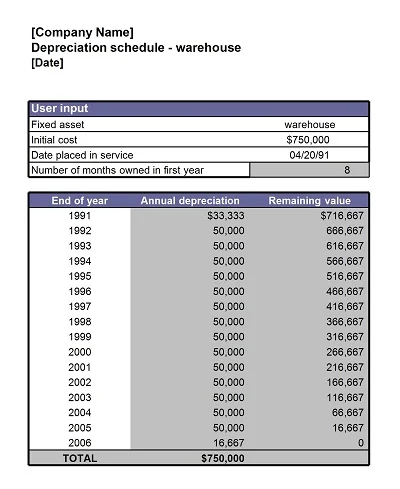
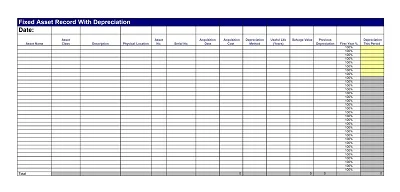
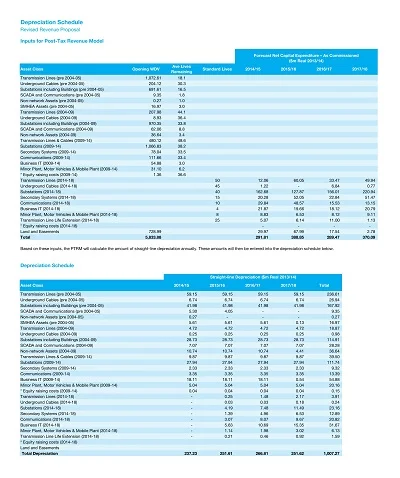
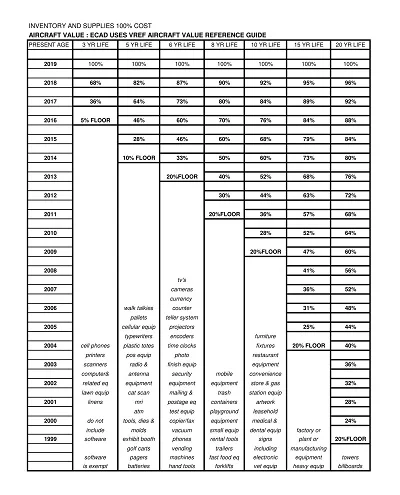
A full depreciation schedule entails all the depreciating assets in a given company. It shows each asset’s name, purchase cost, total depreciation to date, and the net or book value of the asset. It is adjusted annually to reflect current values, but it is elaborated enough to allow for a complete, even if refined, financial picture of the firm.
2. Tax Depreciation Schedule
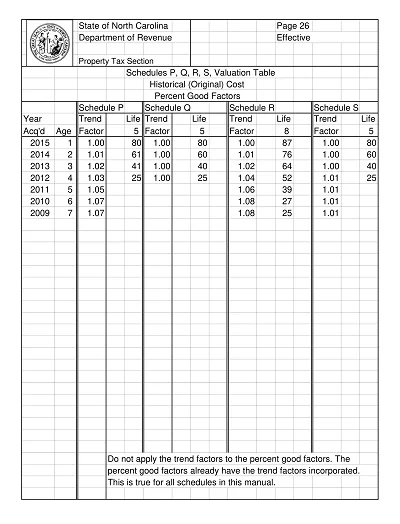
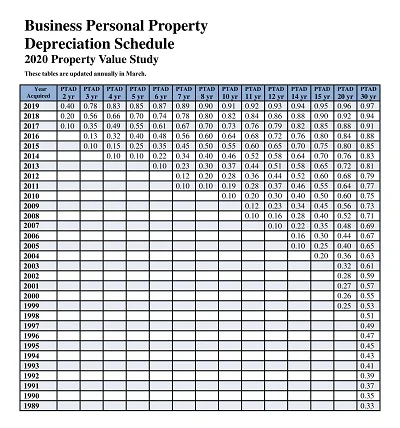
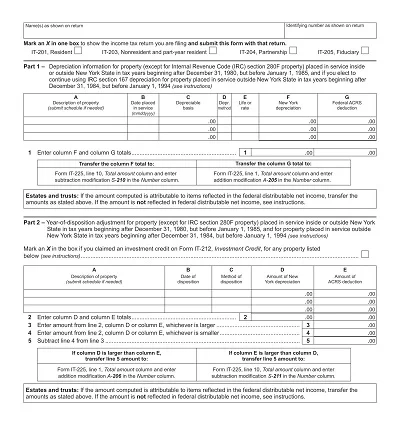
This schedule is prepared to align with relevant taxation laws and graduation for taxation purposes. It complies with the tax laws and contains only details relevant to taxes, like the cost basis for tax, description of accumulated depreciation in conformity with tax laws, and depreciation for tax purposes for the current fiscal year.
3. Component Depreciation Schedule
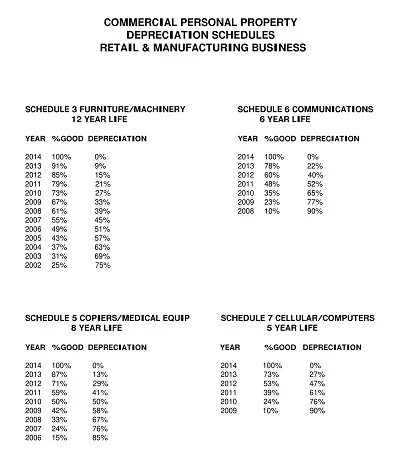
In some cases, the depreciable amount may be applied to each of the large assets, including several major components, whereby each component may be depreciated using the diminishing balance method. This section of the component depreciation schedule acknowledges the fact that different parts of an asset have different useful life and, therefore, different methods of depreciation.
4. Group Depreciation Schedule
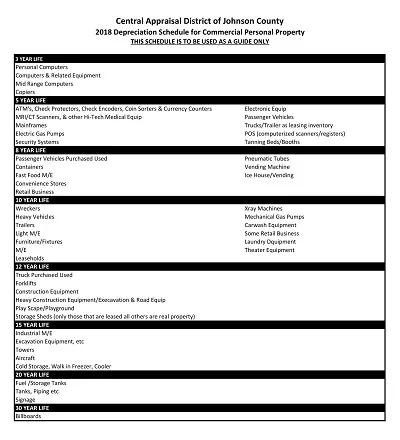
This method of presentation is employed where a company or organization has numerous assets that are most likely to have similar useful lives and rates of depreciation. The investments are grouped together so that depreciation is established on the entire group rather than on such individual elements.
5. International Depreciation Schedule
An international depreciation schedule may suit various accounting and tax requirements that exhibiting companies may meet because of their operations across different countries. The schedule considered reflects the international standards and localized regulations on asset depreciation.
Importance of Depreciation Schedule
There are several reasons why every company needs to have depreciation schedules. They act as the financial road map for business owners by giving them directions on what to do, when, and where to do it regarding asset management.
That is when systematic writing off of the asset’s value over its useful life helps prepare organizations’ planning activities and resource allocation more confidently and efficiently.
Also, depreciation schedules assist firms in planning for taxes by enabling them to make appropriate claims for the depreciation amount on their income, thereby cutting down the amount of tax they are liable to pay.
These schedules also represent the principles of transparent and credible reporting of financial data that can enhance investors’ confidence and meet the demanded standards. Therefore, as suggested earlier, a proper depreciation schedule that is regularly and accurately updated is a prerequisite for managing assets and shaping a stable and financially sound future of an organization.
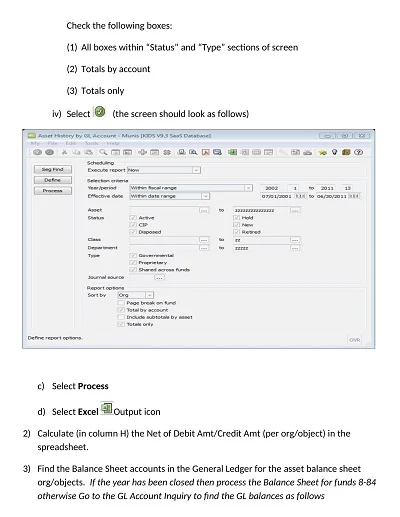
How to use a Depreciation Schedule Template
A nominal depreciation schedule is one of the most effective templates that can help the business determine a decline in the value of assets. Here’s how to effectively use one:
Choose the Right Template
Start by choosing the most appropriate format for preparing accounts for your business that is consistent with the accepted business accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS.
Input Asset Details
For the assets acquired, input all the details on their purchase date, cost, and estimated salvage values.
Select the Depreciation Method
Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of a fixed asset over its estimated useful life in a logical and systematic manner to reflect the costs of using up the asset over that time period which usually involves selecting a method of depreciation that includes the following;
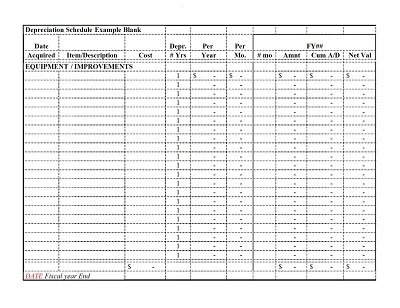
Fill in the Schedule
(6) Enter the amount of depreciation by applying the depreciation method selected above Prepare the primary schedule of fixed assets by calculating the depreciation rates for each period.
Review and Update Regularly
Double-check the calculations to avoid making otherwise unnecessary mistakes in the quantitative data presentation. Change the new master schedule to pick up any asset use, value, and useful life changes.
How to Create a Depreciation Schedule Template
Formulating a depreciation schedule template involves a logical sequence to enable allocating the cost of a given asset over the useful life it is expected to have. To construct this template:
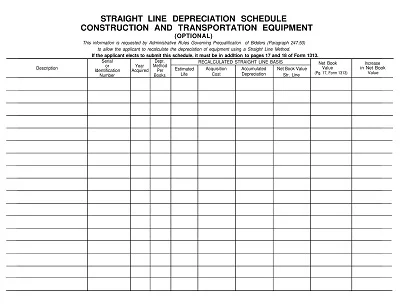
- Select the Method of Depreciation: Select one out of straight-line, declining-balance, and sum-of-the-years’-digits, according to your necessity in the business world.
- Determine Asset Information: Easy to use: Collect all data concerning the asset, such as cost, value at the end of the valuable life, and helpful life.
- Structure the Template: To accommodate this new concept, arrange your Excel in the following manners; Date, Asset Name, Cost, Accumulated Depreciation, Annual Depreciation Expense, and Net Book Value.
- Insert Formulas: When using Excel, perform formulas that can determine depreciation for each period, accumulation of depreciation, and the book value for the asset.
- Test Your Template: Input arbitrary sample asset data into 2 and 3 to verify whether the above equations function properly.
The simple structure provided here, besides enabling a rigid structure of record-keeping, is flexible enough to accommodate various depreciation methods and reporting standards.